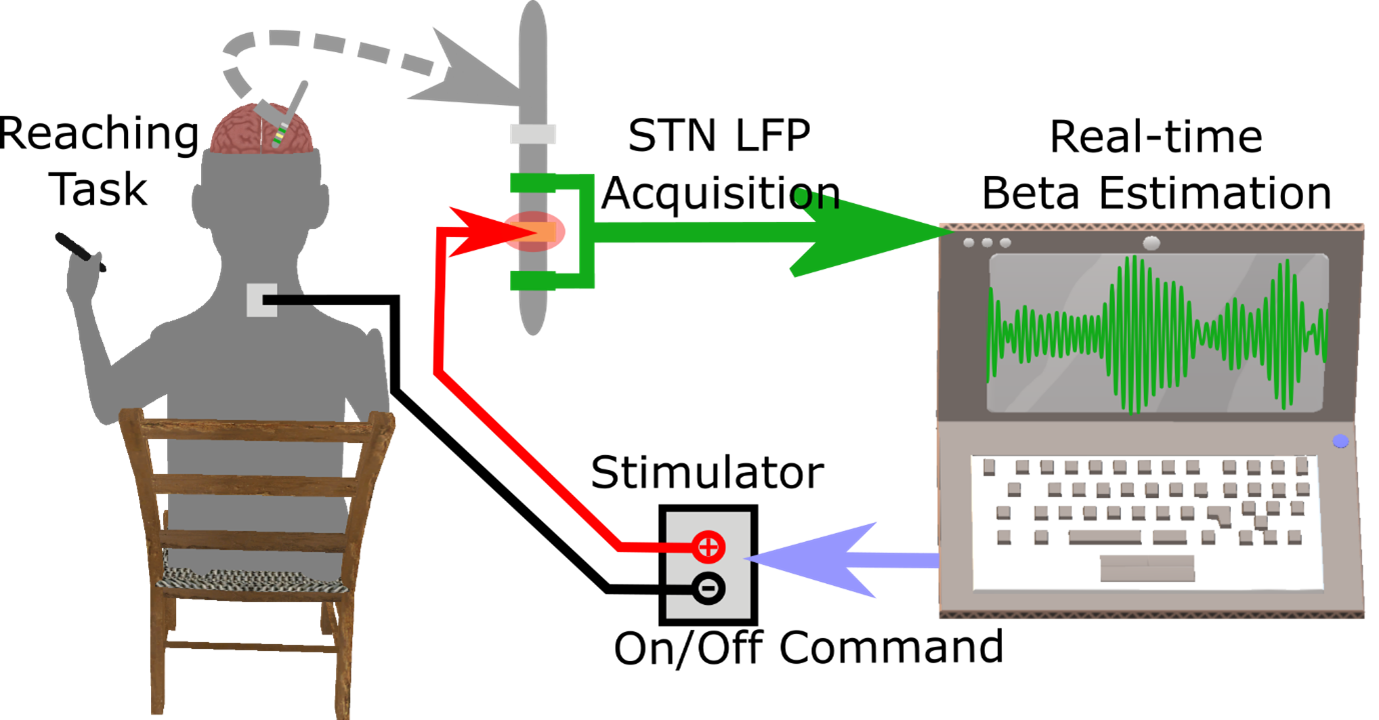
Beta-triggered adaptive deep brain stimulation during reaching movement in Parkinson's disease.
In people with Parkinson’s disease, we compared adaptive deep brain stimulation (DBS) to continuous DBS. The adaptive DBS was triggered by brain wave activity at frequencies called ‘beta’, detected in the subthalamic nucleus region. The two types of DBS were equally effective at improving reaching arm movements, while adaptive DBS was less disruptive of higher-frequency waves, called 'gamma', occurring during these movements.
Scientific Abstract
Similar content
A clinical grade neurostimulation implant for hierarchical control of physiological activity
DyNeuMo Mk-1: Design and Pilot Validation of an Investigational Motion-Adaptive Neurostimulator with Integrated Chronotherapy
Beta-triggered adaptive deep brain stimulation during reaching movement in Parkinson’s disease
1:2 entrainment is not a device-induced artefact, except when it is.
Beta-triggered adaptive deep brain stimulation during reaching movement in Parkinson's disease.
In people with Parkinson’s disease, we compared adaptive deep brain stimulation (DBS) to continuous DBS. The adaptive DBS was triggered by brain wave activity at frequencies called ‘beta’, detected in the subthalamic nucleus region. The two types of DBS were equally effective at improving reaching arm movements, while adaptive DBS was less disruptive of higher-frequency waves, called 'gamma', occurring during these movements.
Scientific Abstract
Citation
DOI
Free Full Text at Europe PMC
PMC10690014Downloads