Spatiotemporal signal space separation for regions of interest: Application for extracting neuromagnetic responses evoked by deep brain stimulation.
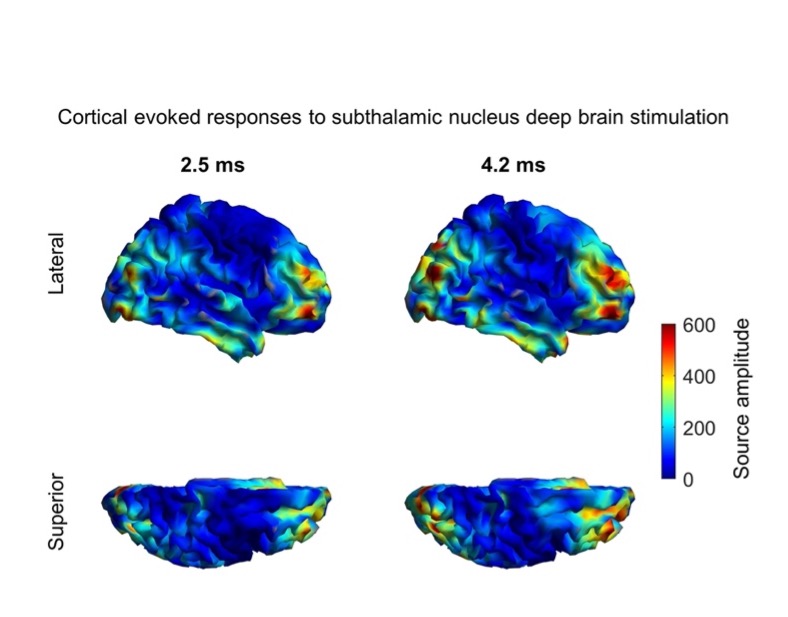
Magnetoencephalography (MEG) is a non-invasive imaging technique which allows us to understand how brain networks are modulated by therapies such as Deep Brain Stimulation (DBS). Major drawbacks of MEG are: 1) high sensitivity to DBS artefacts, and 2) limited spatial resolution due to the spread of inferred brain activity. We develop techniques to address these shortcomings and reveal how DBS may modulate brain networks at short timescales.
Scientific Abstract
Similar content
Dopamine and the dynamics of subthalamic and leg muscle activities in parkinsonian stepping.
Essential Tremor Disrupts Rhythmic Brain Networks During Naturalistic Movement
Beta Burst Characteristics and Coupling within the Sensorimotor Cortical-Subthalamic Nucleus Circuit Dynamically Relate to Bradykinesia in Parkinson's Disease.
Essential tremor disrupts rhythmic brain networks during naturalistic movement.
Spatiotemporal signal space separation for regions of interest: Application for extracting neuromagnetic responses evoked by deep brain stimulation.
Magnetoencephalography (MEG) is a non-invasive imaging technique which allows us to understand how brain networks are modulated by therapies such as Deep Brain Stimulation (DBS). Major drawbacks of MEG are: 1) high sensitivity to DBS artefacts, and 2) limited spatial resolution due to the spread of inferred brain activity. We develop techniques to address these shortcomings and reveal how DBS may modulate brain networks at short timescales.
Scientific Abstract
Citation
DOI
Free Full Text at Europe PMC
PMC10826894External Content
Downloads