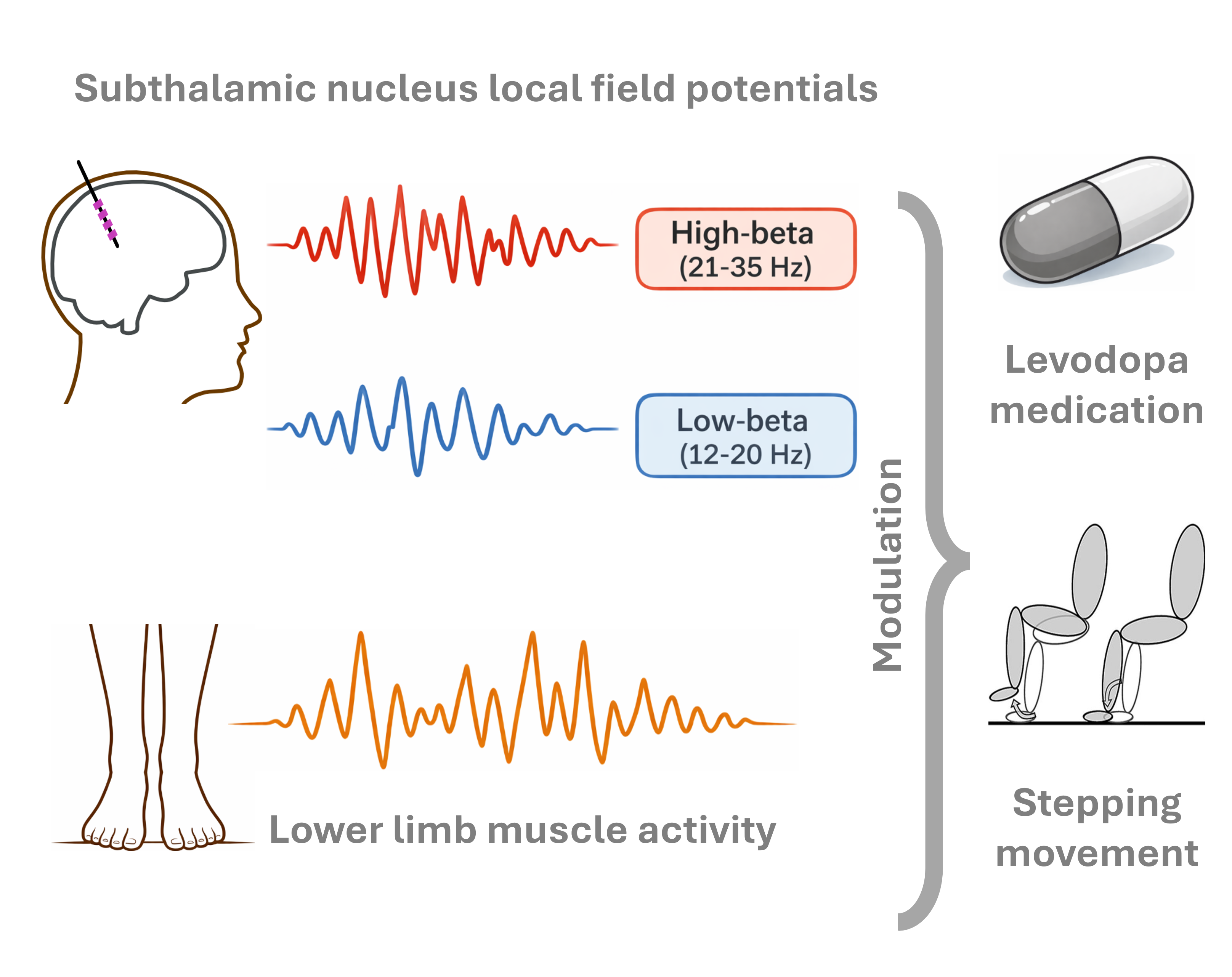
Dopamine and the dynamics of subthalamic and leg muscle activities in parkinsonian stepping.
Freezing of gait is a common and disabling problem in Parkinson’s disease that causes sudden difficulty walking and increases falls. This study measured brain signals from the subthalamic nucleus and leg muscle activity while patients sat, stood, or stepped, with and without levodopa. We found that low- and high-beta rhythms change differently with movement and medication, suggesting distinct roles. Levodopa had stronger effects at step initiation, informing step-timed stimulation strategies to improve gait.
Scientific Abstract
Similar content
Essential Tremor Disrupts Rhythmic Brain Networks During Naturalistic Movement
Beta Burst Characteristics and Coupling within the Sensorimotor Cortical-Subthalamic Nucleus Circuit Dynamically Relate to Bradykinesia in Parkinson's Disease.
Essential tremor disrupts rhythmic brain networks during naturalistic movement.
Cortical beta oscillations help synchronise muscles during static posture holding in healthy motor control.
Dopamine and the dynamics of subthalamic and leg muscle activities in parkinsonian stepping.
Freezing of gait is a common and disabling problem in Parkinson’s disease that causes sudden difficulty walking and increases falls. This study measured brain signals from the subthalamic nucleus and leg muscle activity while patients sat, stood, or stepped, with and without levodopa. We found that low- and high-beta rhythms change differently with movement and medication, suggesting distinct roles. Levodopa had stronger effects at step initiation, informing step-timed stimulation strategies to improve gait.
Scientific Abstract
Citation
DOI
Downloads