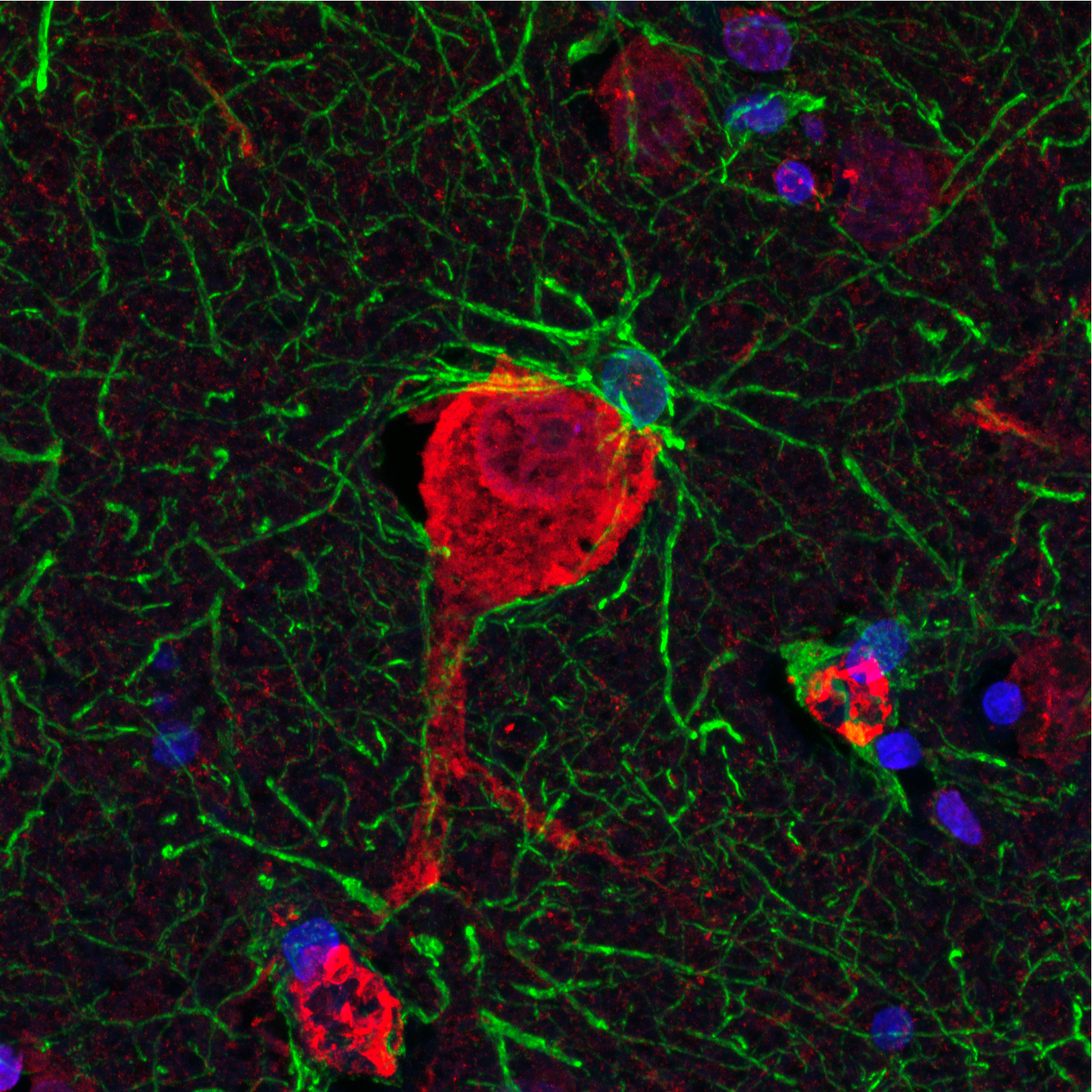
Rapid modulation of striatal cholinergic interneurons and dopamine release by satellite astrocytes.
Astrocytes are brain cells that support nerve cells. Here, we show that astrocytes can rapidly influence the activity of nerve cells called cholinergic interneurons. Astrocytes and cholinergic interneurons are closely positioned, allowing both to work together to control release of the chemical messenger dopamine. These discoveries reveal a powerful form of astrocyte-nerve cell communication.
Scientific Abstract
Similar content
Anxa1+ dopamine neuron vulnerability defines prodromal Parkinson’s disease bradykinesia and procedural motor learning impairment
Selective innervation of subpopulations of striatal neurons by distinct sets of neurons of the external globus pallidus
Selective innervation of subpopulations of striatal neurons by distinct sets of neurons of the external globus pallidus
Rapid modulation of striatal cholinergic interneurons and dopamine release by satellite astrocytes.
Astrocytes are brain cells that support nerve cells. Here, we show that astrocytes can rapidly influence the activity of nerve cells called cholinergic interneurons. Astrocytes and cholinergic interneurons are closely positioned, allowing both to work together to control release of the chemical messenger dopamine. These discoveries reveal a powerful form of astrocyte-nerve cell communication.
Scientific Abstract
Citation
DOI
Free Full Text at Europe PMC
PMC11577008Downloads