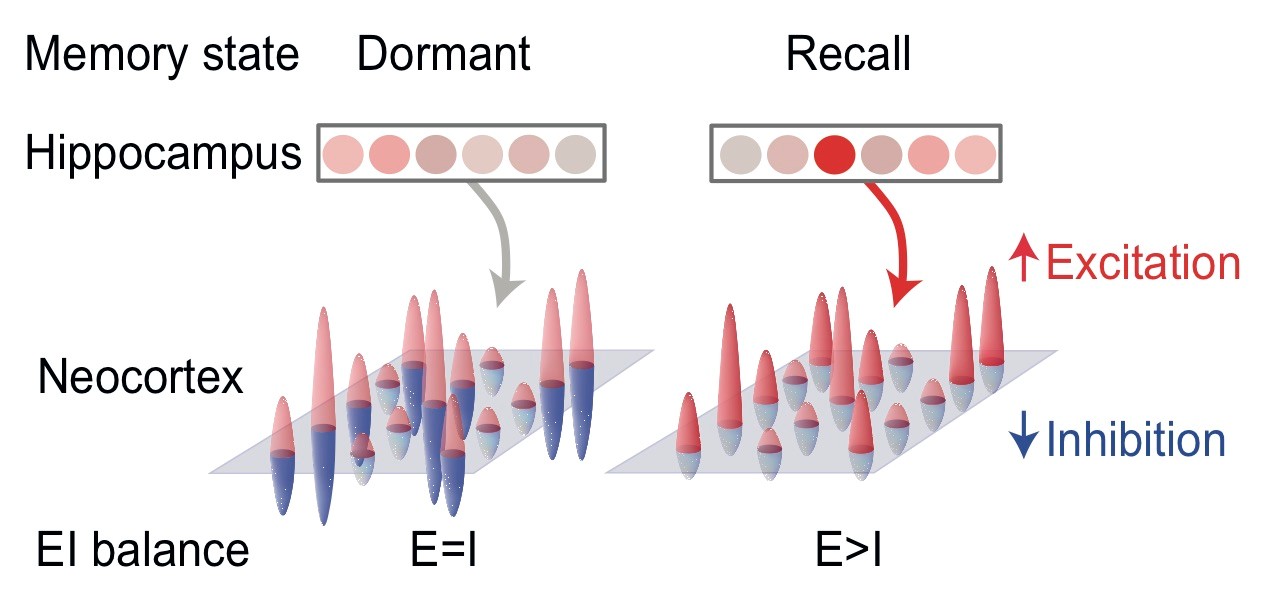
Memory recall involves a transient break in excitatory-inhibitory balance.
The brain has a remarkable capacity to acquire and store memories that can later be selectively recalled. How nerve cells work together for selective memory recall is unclear. We show in humans that memory recall involves brief changes in the balance between different types of signalling (‘excitation’ and ‘inhibition’) in a brain area called sensory cortex. These changes are predicted by activity in another brain region called the hippocampus.
Scientific Abstract
Similar content
A learning-evoked slow-oscillatory architecture paces population activity for offline reactivation across the human medial temporal lobe
Memory reactivation during rest forms shortcuts in a cognitive map.
tDCS induced GABA change is associated with the simulated electric field in M1, an effect mediated by grey matter volume in the MRS voxel
A Checklist for Assessing the Methodological Quality of Concurrent tES-fMRI Studies (ContES Checklist): A Consensus Study and Statement
Memory recall involves a transient break in excitatory-inhibitory balance.
The brain has a remarkable capacity to acquire and store memories that can later be selectively recalled. How nerve cells work together for selective memory recall is unclear. We show in humans that memory recall involves brief changes in the balance between different types of signalling (‘excitation’ and ‘inhibition’) in a brain area called sensory cortex. These changes are predicted by activity in another brain region called the hippocampus.
Scientific Abstract
Citation
DOI
Free Full Text at Europe PMC
PMC8516417Downloads