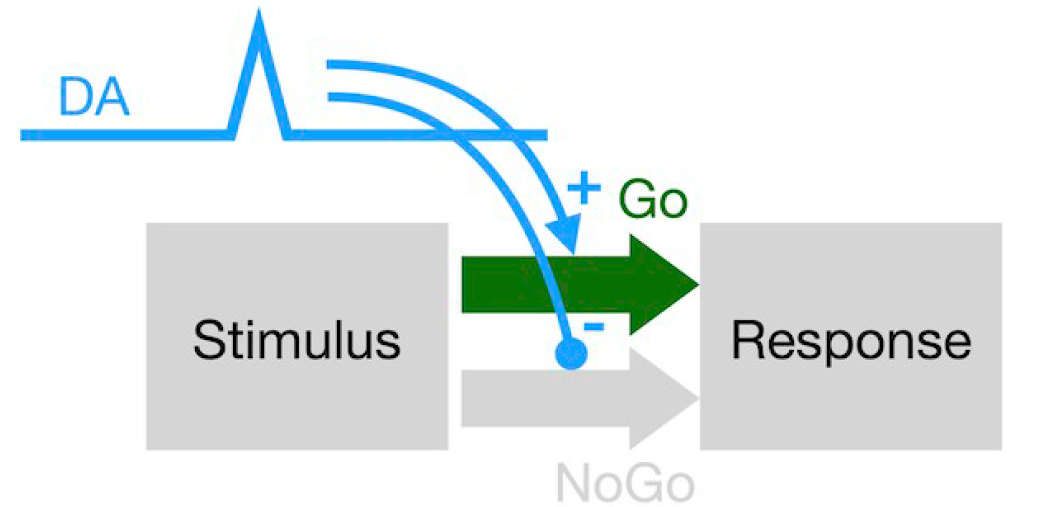
An association between prediction errors and risk-seeking: Theory and behavioral evidence.
Unexpected rewards lead to release of the chemical messenger dopamine in the brain. Interestingly, dopamine is also known control our willingness to take risks. We theorized that, since pleasant surprises cause dopamine release, they might change risk preferences as well. In this study, we tested this idea and discovered that participants are more likely to make a risky choice just after they experienced an outcome that was better than expected.
Scientific Abstract
Similar content
Dithering suppresses half-harmonic neural synchronisation to photic stimulation in humans
Striatal dopamine reflects individual long-term learning trajectories
Benchmarking Predictive Coding Networks - Made Simple
An association between prediction errors and risk-seeking: Theory and behavioral evidence.
Unexpected rewards lead to release of the chemical messenger dopamine in the brain. Interestingly, dopamine is also known control our willingness to take risks. We theorized that, since pleasant surprises cause dopamine release, they might change risk preferences as well. In this study, we tested this idea and discovered that participants are more likely to make a risky choice just after they experienced an outcome that was better than expected.
Scientific Abstract
Citation
DOI
Free Full Text at Europe PMC
PMC8318232Downloads