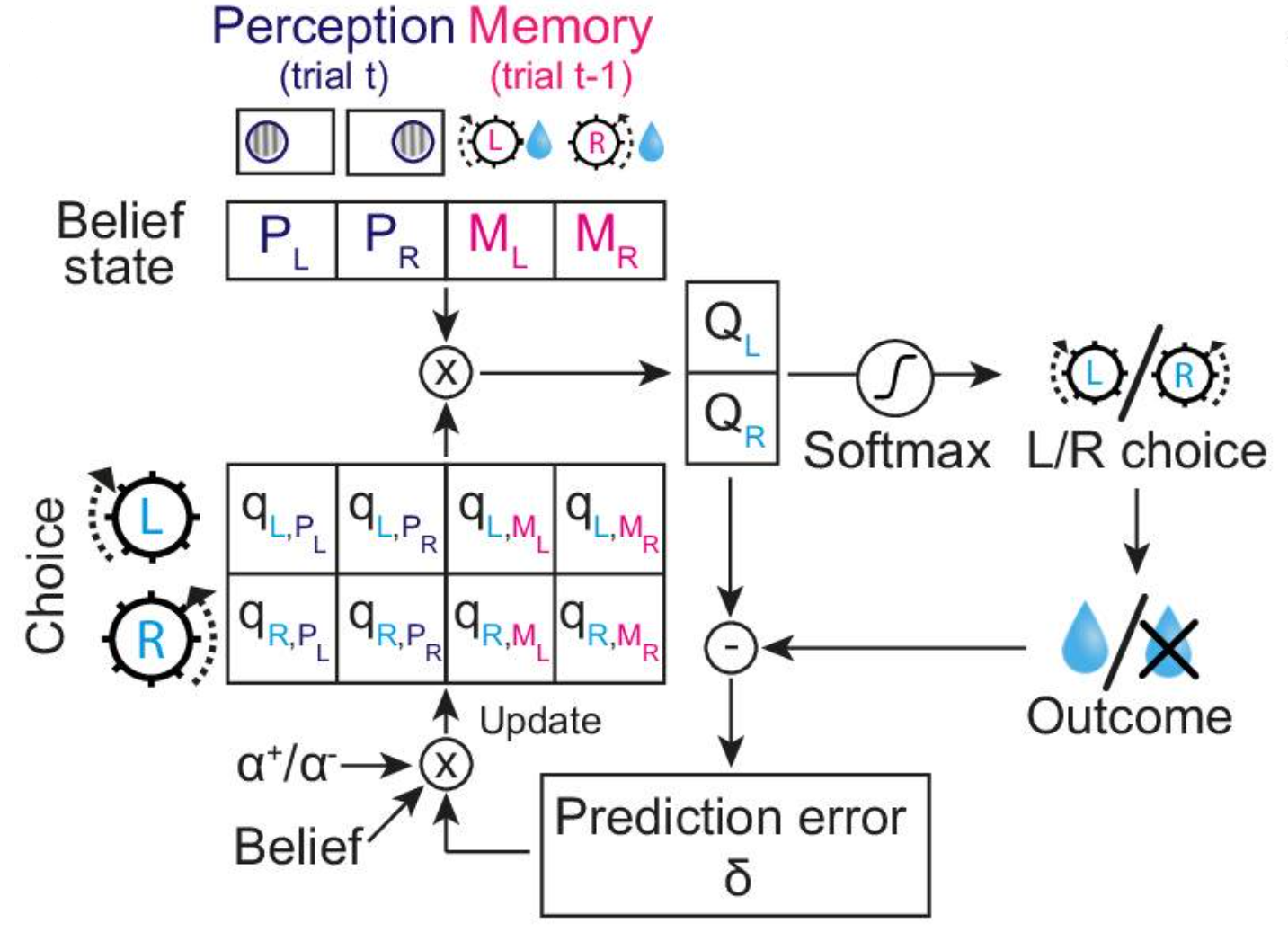
Temporal regularities shape perceptual decisions and striatal dopamine signals.
To optimize behaviour, animals and humans may learn about temporal regularities present in the environment. For example, a traffic light that recently turned green can be expected to remain green for a while. Conversely, a yellow traffic light can rapidly change to red, thus prompting a driver to decelerate. This paper presents experiments shedding light on how our brains learn about such temporal regularities to adjust behaviour appropriately.
Scientific Abstract
Similar content
Striatal dopamine reflects individual long-term learning trajectories
Benchmarking Predictive Coding Networks - Made Simple
Predictive Coding Model Detects Novelty on Different Levels of Representation Hierarchy.
Temporal regularities shape perceptual decisions and striatal dopamine signals.
To optimize behaviour, animals and humans may learn about temporal regularities present in the environment. For example, a traffic light that recently turned green can be expected to remain green for a while. Conversely, a yellow traffic light can rapidly change to red, thus prompting a driver to decelerate. This paper presents experiments shedding light on how our brains learn about such temporal regularities to adjust behaviour appropriately.
Scientific Abstract
Citation
DOI
Free Full Text at Europe PMC
PMC11330509Downloads