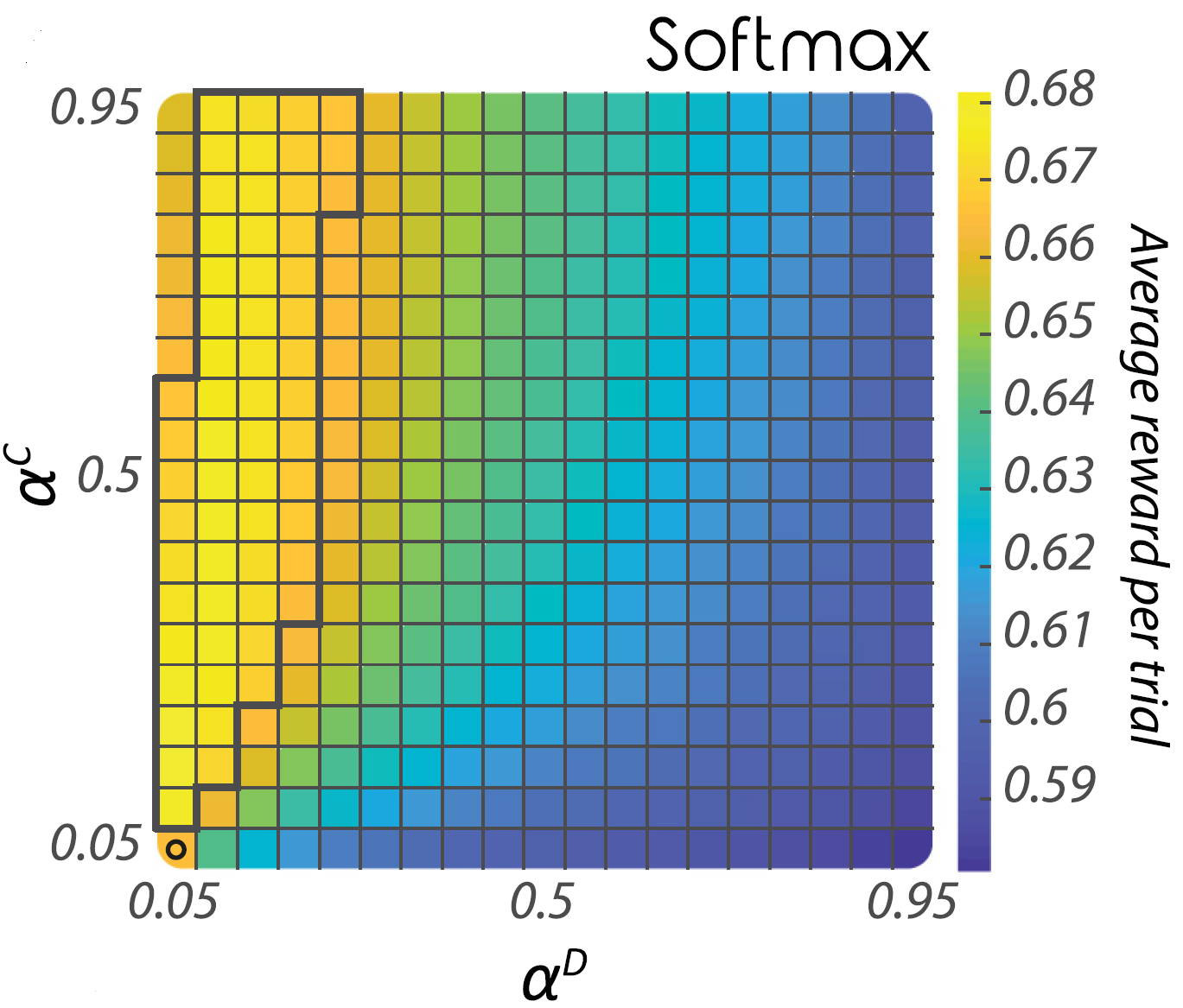
A Normative Account of Confirmation Bias During Reinforcement Learning.
Confirmation bias refers to our tendency to pay more attention to information consistent with our past experience or beliefs. Here, we used computer simulations to investigate whether and how confirmation bias can be useful in certain situations. We show that confirmation bias can enable more accurate decisions in the face of variability, because it leads to higher levels of confidence and helps ensure choices are less likely to be swayed by variability.
Scientific Abstract
Similar content
Striatal dopamine reflects individual long-term learning trajectories
Benchmarking Predictive Coding Networks - Made Simple
Predictive Coding Model Detects Novelty on Different Levels of Representation Hierarchy.
A Normative Account of Confirmation Bias During Reinforcement Learning.
Confirmation bias refers to our tendency to pay more attention to information consistent with our past experience or beliefs. Here, we used computer simulations to investigate whether and how confirmation bias can be useful in certain situations. We show that confirmation bias can enable more accurate decisions in the face of variability, because it leads to higher levels of confidence and helps ensure choices are less likely to be swayed by variability.
Scientific Abstract
Citation
DOI
Free Full Text at Europe PMC
PMC7612695Downloads