The Hippocampus and Neocortical Inhibitory Engrams Protect against Memory Interference.
Our experiences of everyday life often overlap, yet we are able to selectively recall individual memories to guide our behaviour. Here, we investigated how overlapping memories are protected from interfering with each other. Using non-invasive brain imaging and stimulation in healthy human volunteers, we show that two brain areas, the hippocampus and cortex, play an important role in guarding memories.
Scientific Abstract
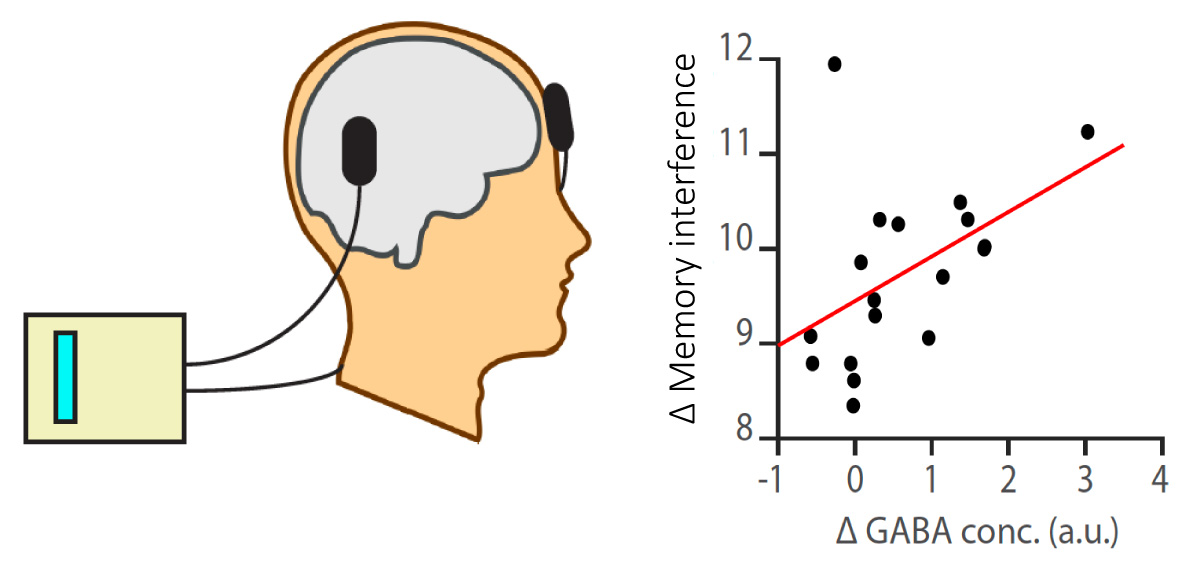
Our experiences often overlap with each other, yet we are able to selectively recall individual memories to guide decisions and future actions. The neural mechanisms that support such precise memory recall remain unclear. Here, using ultra-high field 7T MRI we reveal two distinct mechanisms that protect memories from interference. The first mechanism involves the hippocampus, where the blood-oxygen-level-dependent (BOLD) signal predicts behavioral measures of memory interference, and representations of context-dependent memories are pattern separated according to their relational overlap. The second mechanism involves neocortical inhibition. When we reduce the concentration of neocortical GABA using trans-cranial direct current stimulation (tDCS), neocortical memory interference increases in proportion to the reduction in GABA, which in turn predicts behavioral performance. These findings suggest that memory interference is mediated by both the hippocampus and neocortex, where the hippocampus separates overlapping but context-dependent memories using relational information, and neocortical inhibition prevents unwanted co-activation between overlapping memories.
Similar content
Memory reactivation during rest forms shortcuts in a cognitive map.
tDCS induced GABA change is associated with the simulated electric field in M1, an effect mediated by grey matter volume in the MRS voxel
A Checklist for Assessing the Methodological Quality of Concurrent tES-fMRI Studies (ContES Checklist): A Consensus Study and Statement
A mechanism for hippocampal memory recall based on excitatory-inhibitory fluctuations in neocortex
The Hippocampus and Neocortical Inhibitory Engrams Protect against Memory Interference.
Our experiences of everyday life often overlap, yet we are able to selectively recall individual memories to guide our behaviour. Here, we investigated how overlapping memories are protected from interfering with each other. Using non-invasive brain imaging and stimulation in healthy human volunteers, we show that two brain areas, the hippocampus and cortex, play an important role in guarding memories.
Scientific Abstract
Our experiences often overlap with each other, yet we are able to selectively recall individual memories to guide decisions and future actions. The neural mechanisms that support such precise memory recall remain unclear. Here, using ultra-high field 7T MRI we reveal two distinct mechanisms that protect memories from interference. The first mechanism involves the hippocampus, where the blood-oxygen-level-dependent (BOLD) signal predicts behavioral measures of memory interference, and representations of context-dependent memories are pattern separated according to their relational overlap. The second mechanism involves neocortical inhibition. When we reduce the concentration of neocortical GABA using trans-cranial direct current stimulation (tDCS), neocortical memory interference increases in proportion to the reduction in GABA, which in turn predicts behavioral performance. These findings suggest that memory interference is mediated by both the hippocampus and neocortex, where the hippocampus separates overlapping but context-dependent memories using relational information, and neocortical inhibition prevents unwanted co-activation between overlapping memories.
Citation
Free Full Text at Europe PMC
PMC6560047Downloads